Пол пациента:
Тип патологии:
Область исследования:
Методы исследования:
- https://radiomed.ru/sites/default/files/styles/case_slider_image/public/user/1/stei0011.jpg?itok=gL263eB_
- https://radiomed.ru/sites/default/files/styles/case_slider_image/public/user/1/stei0037.jpg?itok=F4s3fntV
- https://radiomed.ru/sites/default/files/styles/case_slider_image/public/user/1/stein0015.jpg?itok=dSKswa-n
- https://radiomed.ru/sites/default/files/styles/case_slider_image/public/user/1/stei0025.jpg?itok=VCgrJoW5
- https://radiomed.ru/sites/default/files/styles/case_slider_image/public/user/1/stein0035.jpg?itok=9RluyrPu
- https://radiomed.ru/sites/default/files/styles/case_slider_image/public/user/1/stei0053.jpg?itok=S1B8hXbs
ID:185








Специалисты МРТ, где же вы?
Может возможно регулировать яркость...
Я постарался чуть осветлить.
Теперь хоть видно... но патологии рентгенолог общего профиля не нашел...
каким уровням соответствуют аксиальные срезы?
что насчет спинных мышц, дистрофия?
obada, так точно! Срезы в данном случае значения не имеют, т.к. патологии межпозвонковых дисков нет, а мышцы одинаково выглядят на всем протяжении.
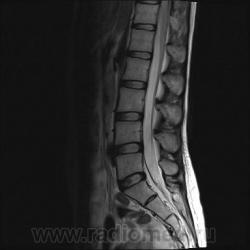
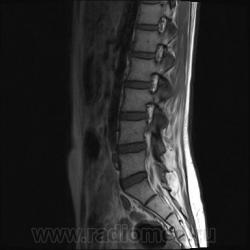
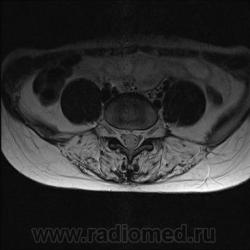
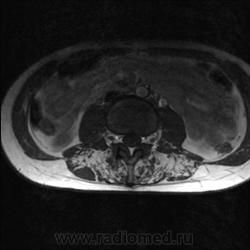
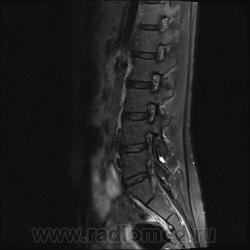
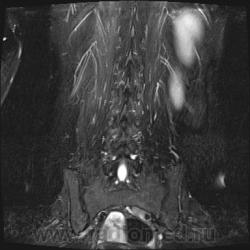
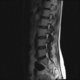
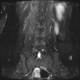
Я специально сделал изображения потемнее, чтобы выделить патологию (жировую дегенерацию) именно мышечной ткани.
В заключении я предположил болезнь Штейнерта. Хотелось бы выслушать мысли коллег.
Добрый админ
Евгений, пожалуйста, поподробнее для начинающих. Что и где нашли, ткните пальцем.
Гм, как это я пропустил эту публикацию... Поясничные мышцы замещены жировой тканью; т.е. Они выглядят "белыми" на Т1 и Т2, в последовательности с подавлением жира, соответственно сигнал уходит; и они "тёмные". Такую картину я видел у пожилых, иногда у пациентов после операции на позвоночнике. По поводу болезни Штейнерта, должна быть клиника, изменения и гипотония/атония мышц других локализаций. На основании только МРТ ПОП не совсем убедительно. Вот небольшая ознакомительная статейка.
Common symptoms in the adult form include:
• myotonia that results in a delay in the ability to relax the muscles after a prolonged contraction,
• muscle weakness of the voluntary muscles, starting gradually and progressing slowly,
• muscle stiffness,
• drooping eyelids,
• unclear pronunciation of words,
• difficulty raising the head when lying,
• difficulty holding an object firmly or lifting it,
• a shuffling gait when walking,
• difficulty climbing stairs or getting up from a seated position
• a long, rather expressionless face.
People with myotonic dystrophy may also have symptoms affecting other parts of the body.
Myotonic Dystrophy (Steinert's disease)
What is myotonic dystrophy?
Myotonic dystrophy, also known as Steinert's disease, is the most common form of muscle disease, affecting approximately one person in 8,000 worldwide. It is a disorder characterized by progressive muscle weakness and wasting and by myotonia (difficulty in relaxing the muscles after they have been contracted). It is a multi-system disease, typically involving a wide range of other tissues as well as muscle.
Who can be affected by myotonic dystrophy?
Anyone can be affected by myotonic dystrophy. It is a genetic disorder passed on to children of either sex by one parent who has the disorder.
Myotonic dystrophy can affect people at any age. The majority of people are diagnosed by the time they reach their early twenties. With each successive generation, the symptoms of myotonic dystrophy seem to get more severe, and the age that they appear gets younger. This phenomenon is known as anticipation.
To the next, even among members of the same family. In most cases, the disorder progresses slowly.
Congenital myotonic dystrophy, the most severe form of myotonic dystrophy, is always present at birth. Affected babies are born to mothers who also have myotonic dystrophy. When the father has myotonic dystrophy, his children are not at risk for the more serious congenital form. Babies with congenital myotonic dystrophy are very weak and floppy and frequently have problems with sucking, feeding and breathing. If they survive the newborn stage, they generally overcome their breathing and
feeding problems, but they are slow to develop language and motor skills and are often affected for life with difficulties in these areas.
What causes myotonic dystrophy?
Myotonic dystrophy is caused by an error in genes located on chromosome 19 or chromosome 3. The basic fault in DM1 is an unstable inherited mutation in the myotonic dystrophy protein kinase gene. At the present time, it is not known how the genetic abnormality causes the disorder.
How is myotonic dystrophy inherited?
Myotonic dystrophy is transmitted via an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. Autosomal refers to the fact that the faulty gene appears on one of the 22 chromosomes not associated with determining the sex of the child (in this case, chromosome 19). Dominant refers to the fact that the disorder is passed down by one parent of either sex who also has the disorder. There is no carrier status. Each child born to an affected parent has a 50% chance of inheriting the disorder.
How is myotonic dystrophy diagnosed?
A physician makes a diagnosis based on family history and a physical examination. Tests that will assist the physician in making his diagnosis include DNA analysis an electromyelogram (to measure electrical activity in the muscle), a muscle biopsy (to study muscle cells for signs of the disease) and in the case of possible cataracts, an eye examination.
What are the symptoms of myotonic dystrophy?
Cataracts may develop frequently in people with myotonic dystrophy. They develop fairly slowly, but can occur in people as young as 30 years.
Myotonic dystrophy may affect the heart muscle. A person may experience palpitations (rapid, bounding pulse) or dizzy spells, or they may have no symptoms whatsoever.
A person who has myotonic dystrophy may have difficulty swallowing. This is due to involvement of smooth (or involuntary) muscle. Cold foods may cause some individuals to choke.
Other potential problems may include bowel problems (constipation and stomach pain) and uterine problems in females. Affected individuals may be susceptible to respiratory problems such as infections and shortness of breath.
Premature balding may occur in some males, while females may experience thinning of their hair. In addition to the symptoms of the adult form, symptoms of the congenital form of myotonic dystrophy include: difficulty breathing, sucking and/or feeding, weakness in virtually all muscles and slowness and difficulty in developing language and motor skills.
All Muscular Dystrophy Canada Information Sheets are available on our website: www.muscle.ca
Ce feuillet d’information est aussi disponible en français. © Muscular Dystrophy Canada 9/07
Updated September 2007 Page 3 of 3
Let me see...
radiographia.ru
Dr.Mario, опередили меня ) Не было возможности выйти в Интернет.
На самом деле, я объясняю свою позицию: мы впервые выявили патологию мышц у молодой пациентки (25 лет) на МРТ, когда смотрели поясничный отдел позвоночника по назначению невролога. Поэтому никак нельзя исключить поражение других мышц, тем более при осмотре пациентки явно видно нарушение осанки и походки. Со слов пациентки (коммуникация осложнялась плохим знанием языка), она страдает не очень давно, сколько - неизвестно, так же как и не известны другие подробности анамнеза.
Публикую этот случай, чтобы посоветоваться с коллегами и выяснить, какие еще заболевания дают подобную картину у молодых пациентов. Dr Mario, хотелось бы услышать Ваше мнение.
Добрый админ
Большое спасибо и Марио за подробные объяснения и Евгению за интересную демонстрацию.
Описанная клиника в принципе укладывается в болезнь Штейнерта, направьте пациентку к невропатологу на полное обследование, электромиографию.
Let me see...
radiographia.ru